Why use a drone in the construction industry?
- Pro products
- Advice
- After-sales service
The use of drones in the construction industry is revolutionizing professional practices, offering a host of advantages such as speed, precision and safety.
Photography & Video
- Site supervision
Photogrammetry
Thermography
- Thermal bridge detection,
- Preventive maintenance
Advanced features
The growing need for innovative solutions
The building and civil engineering (BTP) sector is constantly evolving, and faces many challenges, particularly in terms of efficiency, safety and respect for the environment. To remain competitive, industry professionals are looking for innovative, high-performance solutions capable of meeting these challenges. Among the emerging technologies, drones are emerging as a real revolution for the construction industry. But why use a professional drone in the construction industry?
This article reveals the advantages of using it during the 3 phases in the life of a structure:
– Preliminary phase
– Execution phase, the worksite,
– Operation and maintenance phase.
You'll also discover that the practical applications of this technology are part of a more global digital transition.
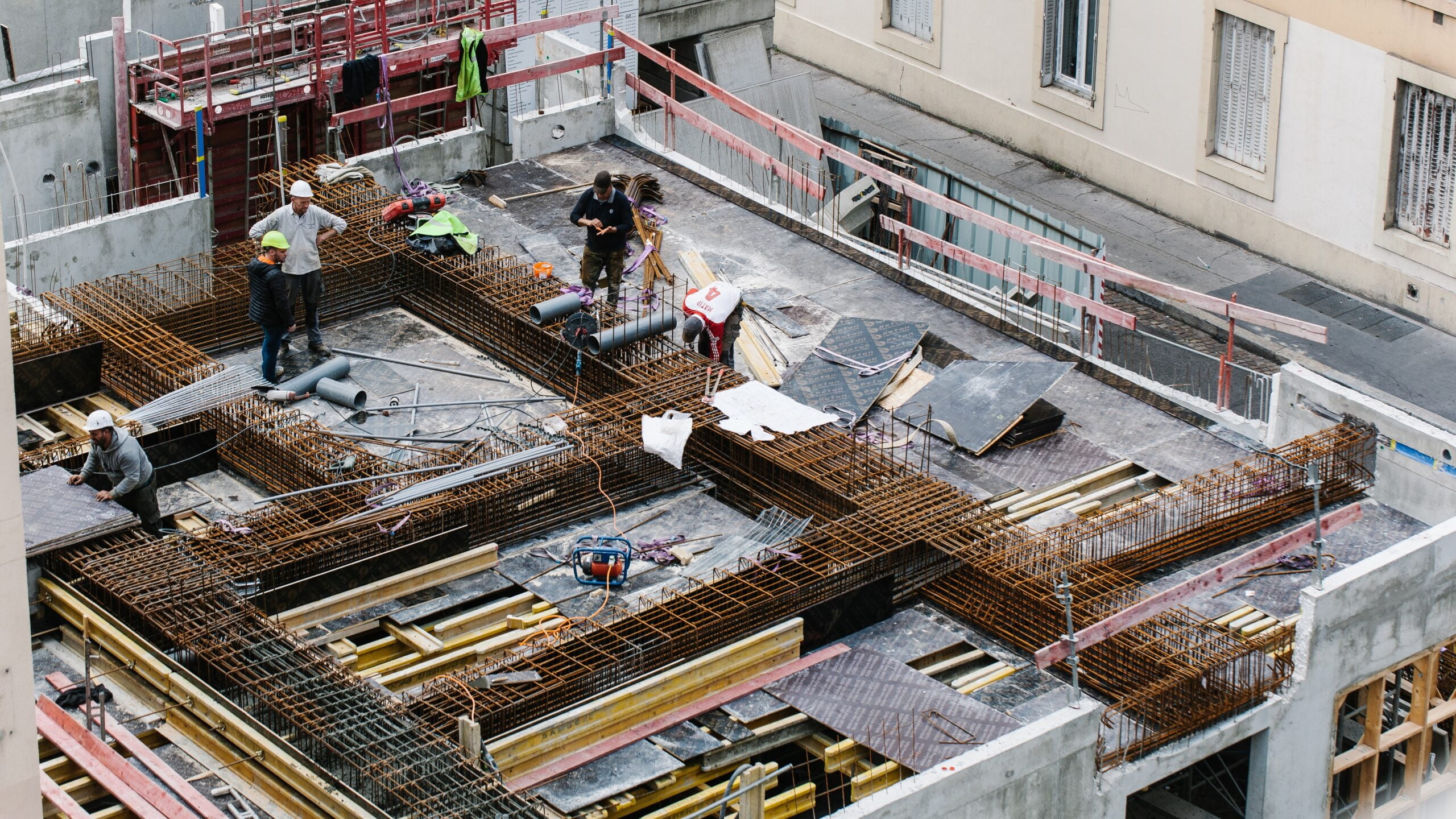

Building and civil engineering applications
Inspection of high-rise or hard-to-reach infrastructures
Drones can be used to inspect all hard-to-reach infrastructures, providing a complete view that cannot be obtained from the ground. They can capture aerial photographs or high-resolution video to detect any defects, cracks or areas of corrosion at a glance, without the need for high-level intervention or costly scaffolding.

Follow-up / site progress with detection of deviations from plans
Always in the form of photographs or videos, aerial shots enable regular site surveys, providing up-to-date imagery of the condition of the site. This makes it possible to compare actual progress with plans, identify any errors or discrepancies, and take swift corrective action if necessary.
Providing a clear, immersive visual perspective, these images can be used to communicate detailed, realistic views of the project to stakeholders such as customers, investors or design teams.
Precise topographical survey of a plot of land
This type of survey is possible using a drone equipped with GNSS sensors, more commonly known as GPS, and photogrammetry. This provides detailed data on the topography of a site, without the need for manual intervention in the field. The level of detail will depend on the quality of the photos taken, and whether or not they are geotagged. Here again, precision will improve as geolocation improves, and additional equipment such as RTK will bring a significant improvement to this need.
Finally, by equipping a drone with a LIDAR, the result becomes exceptional due to the ability of such equipment to provide a very dense point cloud and to penetrate vegetation cover close to the ground.
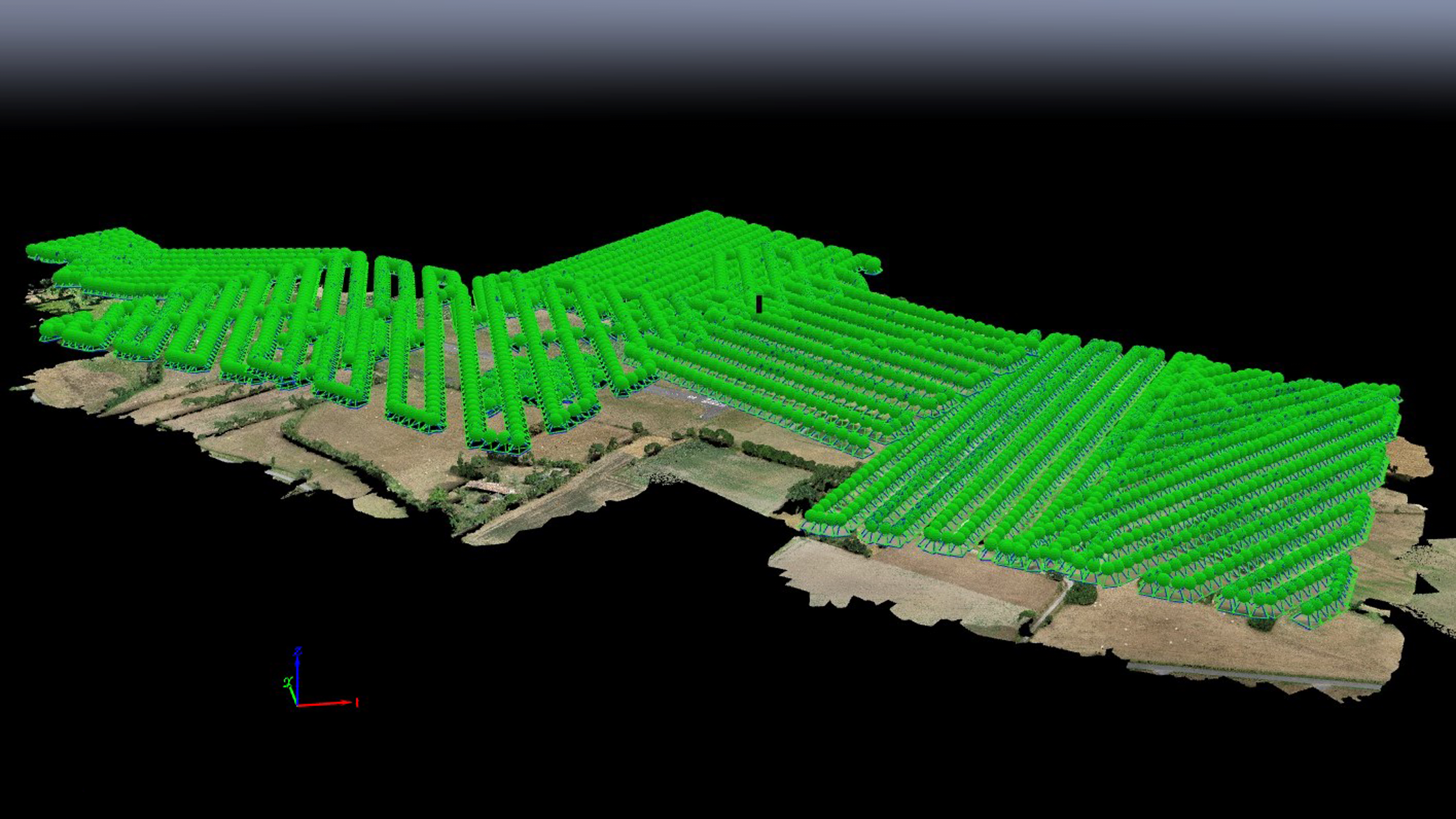
Cubature calculation and accuracy of collected data
This calculation can be the next step after the topographic survey, since it allows you to :
- Determine the volume of soil to be removed or moved to create a flat, level surface,
- when excavating trenches,
- for the management of cuttings and embankments,
- estimate the quantities of materials required, particularly for foundations.
By using a drone for terrain surveying and modeling, construction professionals can obtain accurate, detailed data for cubature calculations. This enables them to plan work, manage resources efficiently, avoid quantification errors and improve the overall accuracy and efficiency of construction projects.

Facade survey
The same photogrammetry technique can also be used to survey facades and produce a 3D image of a complete infrastructure. The accuracy of the image is centimetric, allowing visual access to high areas or overhangs inaccessible to the naked eye when viewed from the ground. In addition to measurements that can be carried out directly on the computer, a professional can also detect various types of faults on the facade, such as cracks, deterioration, water infiltration or structural problems.

Visualization of temperature variations on surfaces
A drone can be equipped with a thermal camera, which can detect and visualize temperature variations to improve preventive maintenance in buildings such as :
- rapid detection of abnormal temperature variations, from hot spots (overheating) in electrical or electronic systems that can lead to fire, to cold zones (heat loss),
- thermal diagnostics which, in the context of the environment and energy transition, can detect thermal bridges, thus highlighting insulation failures.
Drone thermography can be used to document detected problems and, in the context of energy efficiency, track the evolution of a building's thermal condition over time. These maintenance reports provide clear, detailed visual information for owners, building managers and maintenance teams, facilitating work planning and the follow-up of corrective actions.

Benefits
Improving safety on construction sites
Workplace accidents are unfortunately a frequent occurrence in the construction industry. The use of a drone in this context enables :
- Assessment of risks, particularly environmental risks such as unstable zones,
- surveillance and recognition of dangerous situations (e.g. high-rise structures or hard-to-reach areas), which could be coupled with AI,
- search and rescue by providing an overview and quickly targeting areas for intervention,
- site traffic management,
Safety is a business sector in its own right, and is covered in a separate section.
A concrete example: during a roof inspection, a drone can detect anomalies or structural defects without a worker having to climb onto the roof, thus limiting the risk of falls and accidents.

Time-saving and efficient
One of the main advantages of drones in the construction industry is their ability to carry out inspection, measurement and surveillance work quickly. Thanks to their agility and speed, drones can cover vast areas in record time, and do so with unrivalled precision.
For example, during infrastructure construction, a drone can capture images in just a few hours to map the entire site, providing engineers and architects with the precise data they need to optimize their work.
Cost reduction
Drones also deliver substantial savings in the construction industry. In addition to having a much greater environmental impact, their use reduces the cost of renting specialized equipment (cranes, aerial work platforms, etc.), and cuts the duration of worksites thanks to their speed of execution. What's more, the data collected by drones enables us to optimize project planning and management, thereby limiting budget overruns.
Here's a concrete example: when inspecting a building, using a drone to inspect the facades eliminates the need to hire a gondola and reduces labor costs, especially as the aerial images captured by a drone are much faster than those captured by a gondola.
Data quality and accuracy
Drones are equipped with high-resolution sensors and cameras, enabling detailed data to be collected with centimetric precision. This data can be integrated with other technologies, such as :
- Integration with BIM: a precise scan of the terrain can be used as a basis for the design; a scan of the construction site, at regular or specific intervals, superimposed on the BIM model, can be used to detect any discrepancies between what has been achieved and what has been designed;
- The use of AI technologies enables automatic recognition of defects / disorders
Versatility and adaptability
Drones can be fitted with a variety of accessories and sensors, depending on the specific needs of each project. They are thus capable of carrying out a multitude of tasks in the construction industry, such as mapping, thermography, technical inspection, safety, search and rescue.
Here's a concrete example: for a large-scale construction project, a drone can be equipped with a LiDAR sensor for precise mapping of the terrain, then a thermal camera to detect any water or gas leaks before work begins.
An undeniable asset for the construction industry
The use of drones in the construction industry offers many advantages, such as time savings, improved safety, reduced costs, data quality and versatility. These technologies enable industry professionals to meet the challenges they face and remain competitive in a constantly evolving market.
Is the use of drones in the building and civil engineering sector a solution for the future? What other innovations could impact the construction industry in the years to come? Feel free to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below.
FAQ
What is the legal framework for using drones in the construction industry?
By definition, a drone is an aircraft, so its use is governed by the Civil Aviation sector. The legal framework for construction and civil engineering still applies, for example with regard to the wearing of safety equipment.
What new safety issues (physical and psychological) does this new technology bring to the worksite?
New equipment means new risks, and these are taken into account in the training that every user must undergo as soon as a drone weighs 250g, a very serious training course as laid down by the French Civil Aviation Authority.
What are the inherent costs of using a drone (purchase, maintenance, renewal, insurance, training, etc.)?
In terms of price, this increases with the need for quality and precision; the choice is generally made firstly for the sensor, then for the associated drone, accompanied by any modules (such as RTK). Batteries can also play a significant part in the budget. In terms of insurance, a civil liability policy is affordable, while an "equipment breakage" insurance premium can amount to 10% of a drone's value. As far as training is concerned, there are many specialized organizations, so it's important to check in 1er that they meet Civil Aviation criteria.
What external constraints would prevent the drone from being used?
The main constraints are weather conditions (wind strength, visibility, etc.) and regulations: airspace is very busy, and you may need to obtain authorization to fly a drone. Other constraints are more material in nature, such as the presence of metal surfaces that can generate E.M. interactions, or GNSS (more commonly known as GPS) reception problems.
What are the advantages of using drones in the construction industry?
Drones save time, improve safety, reduce costs, provide precise data and adapt to different needs.
How can drones improve safety on construction sites?
Drones can perform potentially dangerous tasks in place of workers, such as inspecting structures at height or hard-to-reach areas.
Do drones save money in the construction industry?
Yes, drones reduce the cost of renting specialized equipment and shorten worksite times thanks to their speed of execution.
What are the different applications for drones in the construction industry?
Drones can be used for mapping, thermography, technical inspection, audiovisual, agriculture, fire safety, search and rescue, and security and surveillance.
How do drones contribute to the quality and accuracy of data collected in the construction industry?
Thanks to their high-resolution sensors and cameras, drones collect precise, detailed data which is then processed and analyzed by specialized software.

Let us help can answer your FAQ or those you forgot to ask.

